C-kielen muuttujatyypit¶
Osaamistavoitteet: Tämän materiaalin läpikäytyäsi tiedät millaisia muuttujatyyppejä C-kielessä yleisesti käytetään.
Muuttujatyypit¶
C-kielen standardeissa on ohjelmoijan iloksi (ja ok, muistinkin säästämiseksi) määritelty valmiiksi joukko muuttujatyyppejä. Muuttujan tyyppi kertookin meille sen käyttötarkoituksen: merkki, kokonaisluku tai liukuluku. Kun muuttujatyyppi on standardoitu, voidaan luottaa, että se toimii kaikissa eri sovelluskehitysympäristöissä ja järjestelmissä samalla tavoin.
| Muuttujan tyyppi | Varattu sana | Tavuja | Standardoitu? |
| Merkki | char | 1 | Kyllä |
| Kokonaisluku (sana) | int | 2 / 4 | Ei, arkkitehtuurin mukaan |
| Lyhyt kokonaisluku | short int | 2 | Kyllä |
| Pitkä kokonaisluku | long int | 4 | Kyllä |
| Yksinkertaisen tarkkuuden liukuluku | float | 4 | Kyllä |
| Kaksinkertaisen tarkkuuden liukuluku | double | 8 | Kyllä |
Voit tarkistaa eri tyyppien koon
sizeof operaattorin avulla.Kokonaisluvut¶
C-kielessä kokonaisluvut luvut esitetään 2-komplementtilukuina. Kokonaislukumuuttujatyypeille luvataan standardin mukaisesti minimi- ja maksimilukualueet, eli kääntäjästä ja tietokoneesta riippumatta muuttujan tulee toimia tällä mainitulla lukualueella. (Huom! standardissa ei täsmälleen koko lukualue ole käytössä)
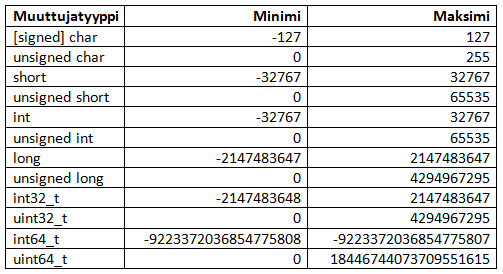
Kokonaislukumuuttujatyyppiä voidaan tarkentaa määreillä:
signed(etumerkillinen), varaa MSB:n etumerkkiä varten kuten aiemmin opittiin. 2-komplementtiluvuissa tämä on siis oletus, joten sitä ei tarvitse erikseen määrätä (paitsi joissain erikoistapauksissa).unsigned(etumerkitön) "vapauttaa" MSB:n mukaan lukualueeseen, jolloin luvut ovat aina positiivisia. Tällöin tietenkin myös lukualue muuttuu vastaavasti.shortjalongovat itseasiassa määreitä, mutta niitä käyttäessä voidaan sanaintjättää pois.constvakioi muuttujan arvon niin ettei sitä ohjelmassa voi muuttaa. Mutta, miksi muuttujan arvo pitäisi voida vakioida? Hyöty on se, että C-kielessä vakiot voidaankin kääntäjän avulla tallentaakin laitteen ohjelmamuistiin RAM-muistin sijasta. Selvää muistinsäästöä, kun tällaisia vakioita voidaan käyttää koodissa muuttujan tavoin.
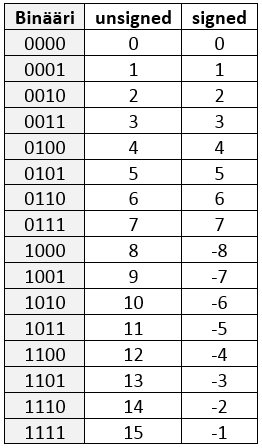
Esimerkkinä. 4-bittisen kokonaisluvun lukualue: unsigned ja signed.
Merkkimuuttuja¶
Merkkimuuttuja
char on siitä kiinnostava tyyppi, että itseasiassa C-kielessä se on vähintään 8-bittinen luku, jonka arvo tulkitaan kääntäjässä kirjoitusmerkiksi ASCII-taulukon mukaisesti. Nyt siis jokaista kirjoitusmerkkiä vastaa numeroarvo C-kielessä. (Tämäkin ratkaisu on perintöä C-kielen kehittäjiltä 1970-luvulta, kun kirjoitusmerkkien erillinen käsittely olisi ollut liian kallista tai muistia vievää.) Tästähän seuraa jänniä. Ohjelmoija voi halutessaan unohtaa
char-tyypin merkkiluonteen ja käyttää sitä (etumerkillisenä) kokonaislukumuuttujana. Tällöin char-tyypin muuttujille toimivat laskutoimitukset kirjaimilla, koska ne tulkitaan kääntäjässä numeroiksi ja ainoastana tulostusvaiheessa kaivetaan esiin vastaava merkki. Eli esimerkiksi laskutoimitukset 'a' + 1 = 'b' (97 + 1 = 98) tai 'c' - 'a' = 2 (99 - 97 = 2). Sulautettuja ohjelmoidessa tästä on itseasiassa valtavasti hyötyä resurssirajoitetuissa laitteissa, kun kirjaimista koostuvia merkkijonoja voidaan käsitellä numeraalisesti, esimerkiksi vertailla kahden sanan "yhtäsuuruutta". Hassua ja kätevää.
C-kielessä on myös rekisteri-, osoitin-, globaaleja ja staattisia muuttujia, mutta niistä lisää myöhemmin.
Johdetut tyypit¶
C-kielen standardissa on määritelty joukko johdettuja muuttujatyyppejä. Käytämme kurssilla tästä eteenpäin näitä muuttujatyyppejä, jotta ohjelmakoodissamme pysyy selkeästi tiedossa käytetyn muuttujan koko.
| Johdettu muuttujatyyppi | Koko tavuina |
| int8_t / uint8_t | 1 |
| int16_t / uint16_t | 2 |
| int32_t / uint32_t | 4 |
| int64_t / uint64_t | 8 |
Muuttujatyyppi
intN_t tarkoittaa etumerkillistä (signed) kokonaislukua ja uintN_t-tyyppi etumerkitöntä (unsigned) kokonaislukua.Voimassa vain C99-standardista. Sun on käytettävä
<stdint.h> kirjastoa. Muuttujien alustaminen¶
Muuttujien alustus tapahtuu, kuten monessa muussakin ohjelmointikielessä, muuttujan esittelyn yhteydessä antamalla muuttujalle arvo.
Esimerkkejä kokonaislukumuuttujan alustamisesta.
int16_t kokonaisluku = -123;
uint16_t etumerkiton_kokonaisluku = 3333;
uint32_t pitka_kokonaisluku = 0x12345678;
double liukuluku = 1.234;
float pienempi_liukuluku = 1.2e-10;
Merkkimuuttujien
char alustuksessa käytetään kirjoitusmerkin erottimena '-merkkiä (heittomerkki) tai numeroa kuten yllä. Muistiin tallentuu sitten kirjoitusmerkkiä vastaava ASCII-taulukon numeroarvo.Nämä alustukset ovat ekvivalentteja
char merkki = 'a'; // Arvoksi a:n ASCII-taulukon numeroarvo
char merkki = 97; // ASCII-taulukossa a:ta vastaa luku 97
Hankaluuksia¶
Koska C on wanha laiteläheinen ohjelmointikieli, jätetään siinä monia asioita ohjelmoijan tietämyksen varaan.
Esimerkki aiheeseen liittyen, jos ohjelmoija yrittää alustaa muuttujan sen lukualueen ulkopuolelta liian isolla luvulla, niin C-kääntäjä kohteliaasti vain varoittaa virheestä.
int8_t a = 1234;
...
warning: overflow in implicit constant conversion.
Mutta mutta! Kääntäjä vain varoittaa virheestä ja ohjelman käännös jatkuu. Tässä on syytä olla tarkkana jottei ajatusvirheet päädy käännettyyn ohjelmaan.
Mitä kääntäjässä sitten tapahtuu - miksi tämä on vain varoitus? Nythän tiedämme että laitteen muistista oli muuttujalle varattu tyypin mukainen määrä tavuja (int8_t on siis yksi tavu). Nyt muuttujaan kirjoitetaankin enemmän tavaraa kuin mahtuu, on seurauksena muistin ylivuoto. Onneksemme C-kielen kääntäjät hoksaavat tämän. Tosin ongelman hoidetaan aika brutaalisti, nimittäin kääntäjät surutta leikkaavat ylimääräiset bitit numerosta pois giljotiinin omaisesti.
Ylläolevassa esimerkissä käy seuraavasti: 1234 on binäärilukuna
10011010010 (11 bittiä). Nyt kääntäjä leikkaa pois ylimmät kolme bittiä 100, jotta alimmat 8 bittiä mahtuvat muistipaikkaan 11010010. Ongelma on, että tämä binääriluku tulkitaankin 2-komplementtilukuna, jolloin muuttujan a alustus onkin kääntäjän mielestä int8_t a = -46 eikä haluttu 1234. Hupsista.Taulukkomuuttujat¶
C-kielessä taulukkomuuttujat esitellään hakasulkujen avulla (kuten monessa muussakin ohjelmointikielessä), joiden sisällä on taulukon koko. Voimme esittää taulukkoja kaikille perusmuuttujatyypeille (ja muillekin muuttujatyypeille joista lisää tuonnempana). Ja tottakai myös moniulotteiset taulukot onnistuvat C-kielessä.
Syntaksi on seuraava:
uint8_t taulukko[5];
uint8_t taulukko[5] = { 1, -3, 5, -7, 9 }; // Alustetaan samalla
uint8_t taulukko[] = { 1, -3, 5, -7, 9 }; // Kääntäjä laskee taulukon koon itse!
uint8_t taulukko[3][3];
uint8_t taulukko [2][3] = { { 1, 2, 3 }, // Alustetaan
{ 4, 5, 6 },
};
uint8_t taulukko [][3] = { { 1, 2, 3 }, // Kääntäjä osaa joskus päätellä taulukon koon!
{ 4, 5, 6 },
{ 7, 8, 9 } };
Merkkijonot¶
Koska C-kielessä ei ole erillistä merkkijono-muuttujatyyppiä, niin merkkijonot ovat char-tyypin taulukkoja. Eli siis ihan vastaavia numeraalisia taulukoita, mutta jotka kääntäjä tulkitsee esittämään ASCII-taulukon mukaisesti kirjoitusmerkkejä.
Merkkijonojen alustuksessa on kuitenkin pientä eleganttia erikoisuutta. Merkkijonojen pitää päättyä aina numeroon
Merkkijonojen käsittely menee tyypillisesti ohjelmassa siis rikki, jos merkkijono ei lopu nollaan.
0, literaaliin '\0'. Tämä on oleellista tietää, koska monet C-kielen standardikirjastojen ja/tai muut valmiit funktiot olettavat aina näin! Merkkijonojen käsittely menee tyypillisesti ohjelmassa siis rikki, jos merkkijono ei lopu nollaan.
Hox! Luku 0 on ihan eri asia (kääntäjän mielestä) kuin ASCII-taulukon merkki '0', jota vastaava numeroarvo on 48.
Merkkijonojen alustus voidaan tehdä usealla tavoin, ihan kuten taulukkojen tapauksessa yllä.
char viesti[] = "Terve"; // Kääntäjä lisää automaattisesti perään 0, taulukon pituus 5+1 merkkiä
char viesti[6] = {'T', 'e', 'r', 'v', 'e', '\0'};
char viesti[] = {'T', 'e', 'r', 'v', 'e', '\0'}; // Kääntäjä osaa laskea taulukon koon
char viesti[] = {84, 101, 114, 118, 101, 0}; // ASCII-taulukon mukaiset merkkikoodit
Jos alustamme merkkijonon / taulukon liian lyhyenä, kääntäjä täyttää sen automaattisesti nollilla. Allaolevat alustukset ovat ekvivalentteja.
char viesti[5] = "T";
char viesti[5] = {'T'};
char viesti[5] = {'T', 0, 0, 0, 0 };
Indeksit¶
Muutoin taulukkojen käsittely on tuttua, niissä liikutaan indeksien avulla kuten muissakin ohjelmointikielissä. Tosin, indeksin ensimmäinen arvo on
0 ja viimeinen sallittu indeksi on taulukon koko-1. Esimerkki indeksien käytöstä.
uint8_t taulukko [3][3] = { { 1, 2, 3 },
{ 4, 5, 6 },
{ 7, 8, 9 } };
for (i=0; i < 3; i++) { // alkiot 0,1,2
for (j=0; j < 3; j++) { // alkiot 0,1,2
printf("%d\n",taulukko[i][j]);
}
}
Taulukoissa voidaan liikkua muillakin tavoin, josta lisää tulevassa materiaalissa Osoittimet. Laiteläheisyys tarjoaa monenlaista kivaa muistinkin käsittelyyn. (Joissain tapauksissa taitava tai myös vähemmän taitava ohjelmoija voi onnistua menemään indeksillä taulukon ulkopuolelle, ilman että kääntäjä sitä huomaisi, joten ollaanpa varovaisia!!)
Muuttujatyyppien muunnokset¶
C-kielessä voidaan muuttujien tyyppiä muuttaa tiettyjen sääntöjen mukaan. Standardi kertoo asiat tarkasti, mutta meille riittää am. yleissäännöt.
- Muunnokset, joissa saatetaan menettää tietoa, aiheuttavat kääntäjässä varoituksen. Esimerkiksi, lukualuetta suuremman arvon muutaminen pienempään muuttujatyyppiin, jolloin kääntäjän giljotiini pudottaa ylimmät bitit.
- Yhteen- ja kertolaskussa voi tulla ylivuoto, jolloin giljotiini leikkaa taas ylimmät bitit pois.
- Yleinen muunnoshierarkia alhaalta ylöspäin: double <- float <- long int <- int <- char.
- Aritmeettisissa operaatiossa perussääntö on, että operandeista hierarkian mukaan "alempi" tyyppi muunnetaan "ylemmäksi" tyypiksi.
- signed tyyppien keskinäisessä muunnoksessa (esim. short -> long) tapahtuu sign extension, eli merkkibitti kopioidaan ylimpiin bitteihin.
- Esimerkki.
int8_t -> int16_t: 11001010 -> 1111111111001010, joka on johdettavissa 2-komplementin esityksestä. - signed-tyypit konvertoidaan unsigned-tyypeiksi kääntäjässä.
- Liukulukujen muunnoksessa kokonaisluvuksi desimaaliosa pudotetaan surutta pois eikä pyöristetä!
- Esimerkiksi muunnos
(int)0.5 = 0. - Merkkimuuttujan char-tyyppi on taas hieman erikoinen. Koska ASCII-merkkejä on 127 kpl, ne voidaan osoittaa 7:llä bitillä. Nyt kun char-ajatellaan 8-bittisenä lukuna, jää meille MSB merkkibitiksi. Tässä on kääntäjissä vaihtelua tulkitaanko char-tyyppi 2-komplementin mukaan negatiiviseksi luvuksi vai 8-bittiseksi positiiviseksi luvuksi.. tämän vuoksi jos haluaa olla ihan varma, voi käyttää numeraalisen ajatellun char:n kanssa määreitä signed tai unsigned.
Esimerkkejä.
uint8_t a = 1234; // Käännettäessä tulee virheilmoitus main.c: In function 'main': main.c:6: warning: large integer implicitly truncated to unsigned type // Yhteenlasku jonka tulos menee lukualueen ympäri // int8_t:n maksimiarvo siis 127 int8_t a = 33; int8_t b = 101; int8_t c = a + b // tulos -122
Tyyppimuunnoksen pakottaminen¶
C-kielessä on tyyppimuunnosoperaattori (engl. cast), jolla muunnos voidaan pakottaa missä tahansa kohtaa koodia. Tätä voidana tarvita, kun esimerkiksi kirjaston funktio haluaa sisäänsä tarkalleen vain tietyn tyyppisiä muuttujia. Muunnosoperaattori on muotoa
(tyyppinimi) lauseke. Esimerkiksi.
uint16_t x = 7;
double y = sqrt((double) x); // tässä x:n arvo pakotetaan double:ksi,
// ennen neliöjuuren laskemista
Muunnosoperaattorilla voidaan rikkoa aiemmin mainittu hierarkia tarvittaessa.
Lopuksi¶
Taulukkojen kanssa tulemme vielä pelaamaan osoitinmuuttujien yhteydessä. Muuttujamuunnoksista ja alustuksissa on hyvä muistaa kääntäjän giljotiini, niin säästytään monelta kummalliselta bugilta.
Anna palautetta
Kommentteja materiaalista?