Tietokoneen toiminta¶
Osaamistavoitteet: Tämän materiaalin läpikäytyäsi tiedät mitä tarkoittaa tietokoneen korkean tason arkkitehtuuri ja organisaatio sekä tunnet tietokoneen yleisen toimintaperiaatteen.
Tietokone on yleiskäyttöinen laite, joka käsittelee numeeris-loogista tietoa toimintaohjeidensa (ts. ohjelman) mukaisesti. Yleiskäyttöisyys tarkoittaa, että tietokone voidaan ohjelmoida suorittamaan erilaisia ohjelmia. Ohjelma koostuu joukosta käskyjä, jotka esitetään suorittimien ymmärtämällä kielellä (ts. konekielellä).
Tietokoneen toimintaperiaate lyhyesti on seuraava: Suoritin / prosessori / keskusyksikkö saa käskyn ja sen tarvitseman datan tietokoneen muistista, suorittaa käskyn annetulle datalle, palauttaa tulokset takaisin muistiin ja hakee seuraavan käskyn ja suorittaa sen, jne. Pelkistetysti tietokone vain suorittaa tätä sykliä kunnes ohjelma päättyy tai virrat katkaistaan. Nyt tämän määritelmän mukaisesti tietokone ei siis tarvitse toimiakseen kuin suorittimen ja muistin.
Tietokoneen organisaatio¶
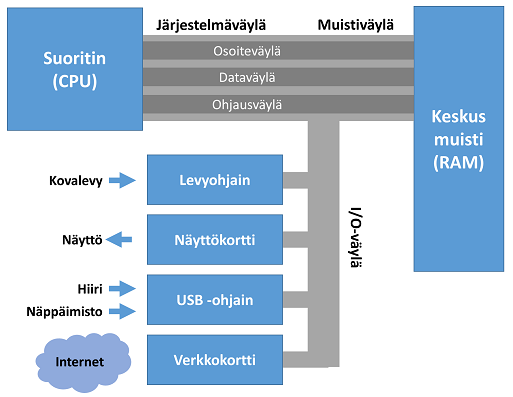
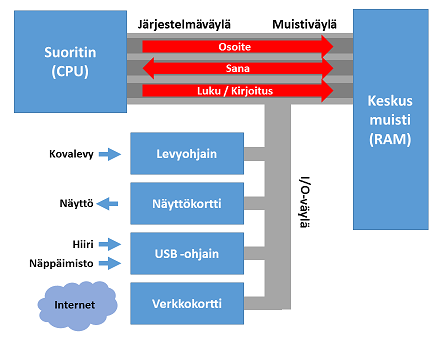
Mutta, kun tietokoneeseen lisätään komponetteja ja oheislaitteita kuten näppäimistö ja näyttö, saadaan ihminen ja ympäröivä maailma liitettyä tietokoneeseen. Tietokonejärjestelmä kuvaa toteutuksen tietokoneen organisaatiosta, eli suorittimen, muistin ja ja oheislaitteiden yhteenliittämisestä/kytkemisestä toimivaksi tietokoneeksi. Oheislaitteet kytketään väylien (joukko sähköisiä johtimia), mahdollistaen tiedonsiirron ja toiminnan ohjauksen eri järjestelmän komponenttien välillä.
Kuvassa yleinen tietokonejärjestelmän korkean tason organisaatio.
Hox! Käytämme tästä eteenpäin tekstissä myös englanninkielisiä termejä ja/tai lyhenteitä. Esitämme suomenkielisen termin yhteydessä usein myös englanninkielisen vastineen. Kaikille termeille ei ole vakiintunutta suomenkielistä käännöstä.)
Suoritin¶
Loogisesti tietokoneen suoritin (prosessori / keskusyksikkö, engl. Central Processing Unit, CPU) jaetaan kahteen osaan:
- Ohjausosan (kontrolliyksikkö, engl. control unit) tehtävänä on ohjata suorittimen ja sitä kautta epäsuorasti tietokoneen toimintaa. Ohjausosa synkronoi suorittimen, muistin ja oheislaitteiden toiminnan niin, että käskyt saadaan suoritettua mahdollisimman tehokkaasti, väyläohjaimen ja oheislaitteiden ohjainten avulla.
- Laskentayksikkö (engl. datapath) sisältää konekielisten käskyjen (ts. suorittimen äidinkieli) suorittamisen toiminnalliset osat kuten aritmeettis-loogisen suoritusyksikön (ALU), suorittimen sisäisen muistin (rekisterit), suorittimen liitynnän järjestelmäväylään sekä muita sisäisiä komponentteja, joilla optimoidaan peräkkäisten käskyjen suoritusta.
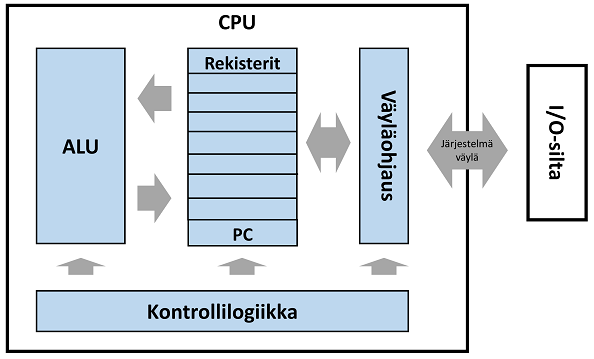
Suoritin toimii pääpiirteissään seuraavasti (noudattaen tietokoneen toimintaperiaatetta):
- Ohjausosa hakee suoritettavat konekieliset käskyt ja niiden tarvitseman datan keskusmuistista (väyläohjauksen avulla).
- Haetut käskyt tulkitaan suoritettavan operaation selvittämiseksi ja ohjausosa datan suorittimen sisäiseen pieneen muistiin (rekisterit).
- Ohjausosa asettaa suorittimen (ja sen oheiskomponenttien) tilan sellaiseksi, että operaatio voidaan suorittaa ALU:ssa rekistereissä olevalle datalle.
- ALU suorittaa käskyn.
- Ohjausosa kirjoittaa käskyn tulokset rekistereihin, josta ne viedään takaisin keskusmuistiin (väyläohjauksen avulla).
Yksittäinen konekielen käsky tekee yleensä hyvin yksinkertaisia asioita, yhden operaation, esimerkiksi yhteenlaskun
add A,B, eli laske yhteen rekisterien A ja B arvot ja tallenna tulos rekisteriin A. Koska suoritin osaa vain omaa konekieltään bittitasolla, jokainen korkeamman tason kielellä (kuten C) laadittu ohjelma on ensin käännetty konekielelle erillisellä käänätäjäohjelmalla. Kuten arvata saattaa, yksittäisen korkean tason kielen käskyn (vaikkapa for-silmukan) toteutus saattaa vaatia satoja rivejä konekieltä ja ohjelmissa on helposti tuhansia rivejä konekieltä..Suorittimen toimintaan ja tehokkuuden optimointiin palaamme tarkemmin kurssin tietokonetekniikan-osuudessa..
Arkkitehtuuri¶
Tietokoneen arkkitehtuuri taas kuvaa, miten tietokoneen organisaatio realisoidaan ohjelmoijalle näkyväksi. Sisältäen esimerkiksi ratkaisut siitä missä muodossa tieto kuvataan suorittimelle, millaisia konekielen käskyjä on käytössä, miten ne esitetään bittitasolla, miten muisti näkyy ohjelmalle, miten suorittimen sisäisiä järjestelmiä käytetään, miten oheislaitteet on kytketty, jne. Kurssilla sivuamme sulautettujen järjestelmien arkkitehtuuria siltä osin, että ymmärrämme resurssirajoitteisessa laitteessa muistin kulutuksen haasteet ja kytkennät oheislaitteisiin (kuten antureihin).
Esimerkiksi, vilkaise sivua 9 tämän pdf-tiedoston Arduinon siruarkkitehtuurista.
Sanan pituus¶
Osana suorittimen arkkitehtuuria, määritellään sen käsittelemän tietoalkion koko. Nyt tietokone osaa käsitellä vain bittejä binäärilukuina (tästä lisää kohta..), joten suorittimelle määritellään sanan pituus joka kertoo suurimman tietoalkion koon minkä suoritin pystyy kerralla yhdellä konekielen käskyllä käsittelemään. Eli mitä isompi sanan koko on, sitä enemmän ja monimutkaisempaa tietoa (=isompia binäärilukuja) suoritin pystyy kerralla käsittelemään.
Esimerkki. Kun arkkitehtuurin sanotaan olevan 8-bittinen, tarkoittaa se, että sanan pituus on 8 bittiä ja näin ollen jokainen tietoalkio kuvataan suorittimelle 8-bittisenä binäärilukuna (esim. 10101101). Vastaavasti jos arkkitehtuuri on 16-bittinen, suoritin osaa käsitellä 16-bittisiä binäärilukuja.
Monimutkaisemman tiedon käsittelyä varten (ja laskentatehon lisäämiseksi) suorittimien arkkitehtuurit kasvavat kokoajan kohti isompaa sanan pituutta, esimerkiksi nyky-PC:t ovat jo 64-bittisiä arkkitehtuuriltaan. Sulautetuissa järjestelmissä näkee vieläkin 8-bittistä suoritinarkkitehtuuria, esimerkiksi Arduinossa on ATmelin 8-bittinen mikrokontrolleri. Nykyään kyllä sulautettujen järjestelmien suorittimet alkavat olla 32-bittisiä, esimerkkinä älypuhelimet. Kurssimme sulautetun laitteen SensorTag:n suoritin on 32-bittinen.
Järjestelmäväylä¶
Järjestelmäväylä (engl. system bus) kytkee siis CPU:n ja ulkoiset komponentit (kuten muistin) toisiinsa. Karkeasti järjestelmäväylä voidaan jakaa muistiväylään ja I/O-väylään, mutta nämä ratkaisut vaihtelevat suorittimesta ja tietokonejärjestelmästä riippuen.
Väylä ajatellaan (ja realisoidaan) joukkona rinnakkaisia sähköisiä johtimia, joihin väylän laitteet kytkeytyvät.

Väylissä yleisesti kulkee kolmentyyppisiä sähköisiä signaaleja (bittejä, joilla on omat johtimet) eli osoite-, data- ja ohjausväylät.
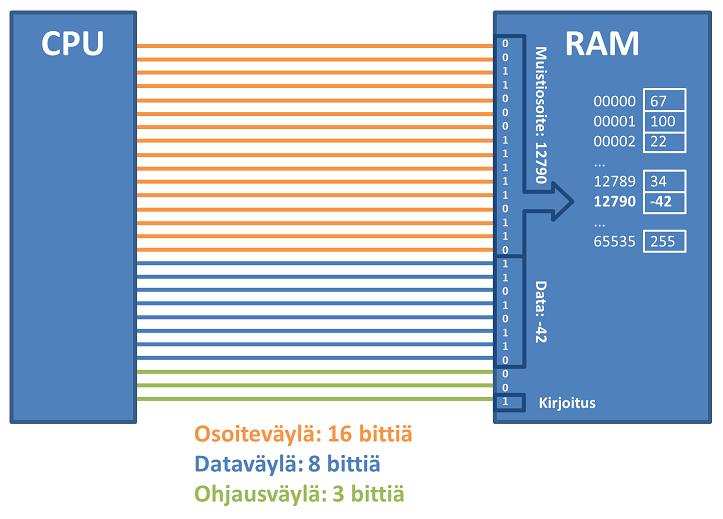
Osoiteväylä ilmaisee tiedonsiirron kohteen osoitteen, esim. muistiosoitteen keskusmuistissa. Osoite siis tarvitaan, jotta haluttu tietoalkio voidaan yksilöidä ja sille voidaan varata muistista tila, jossa sen arvo säilytetään. Muistiosoite itsessään on ihan vaan luku (kuten vaikka katuosoitteessa), jonne haluttu tieto viedään talteen. Esimerkiksi, taloon numero 3 voidaan viedä 16-bittinen luku talteen ja myöhemmin sitä tarvittaessa haetaan se ohjelmaan käyttöön.
Itse osoite muodostetaan tulkitsemalla sähköisissä johtimissa oleva jännite bitteinä (siis joko 0 tai 1). Kun väylän johtimet ovat rinnakkain, ja jokainen niistä edustaa yhtä bitin arvoa, saadaan väylältä luettua sen leveyden kokoinen binääriluku. Jos väylässä on 16 johdinta, voidaan siis osoitteena käyttää 16-bittistä binäärilukua.
Esimerkki. Kun osoiteväylän leveys on 16 bittiä, muistissa on 2^16 = 65536 muistipaikkaa, eli muistiosoitteet 0-65535. Tietokoneessa ensimmäinen muistiosoite on aina 0. Yo. kuvassa osoiteväylän biteistä saatu muistipaikan osoite on binääriluku 0011000111110110, eli kymmenjärjestelmän lukuna 12790.
Dataväylässä taas kulkee kaksisuuntaisesti siirrettävä data, siis joko suorittimelta muistiin tai muistista suorittimelle. Vastaavasti dataväylän rinnakkaisten linjojen määrä, ts. leveys, heijastaa sanan pituutta. Nyt koko tietoalkio saadaan haettua suorittimelle kerralla. 8-bittisessä arkkitehtuurissa dataväylässä on 8 rinnakkaista linjaa ja 32-bittisessä arkkitehtuurissa dataväylässä on 32 linjaa. (Okei, on olemassa myös ratkaisuja hakea väylänleveyttä isompia tietoalkioita, mutta tässä esitämme perusidean.)
Nyt yo. kuvassa 8-bittisen dataväylän bitit tulkitaan binääriluvuksi 11010110 joka on kymmenjärjestelmässä -42. (Binäärilukunen tulkitsemisesta lisää ensi luennolla..)
Ohjausväylän signaalit ohjaavat (väylän kautta) suorittimen ja oheislaitteiden toimintaa. Esimerkiksi kertovat muistille suoritettavan operaation (luku / kirjoitus) tai aktivoivat valitun digitaalipiirin/oheislaitteen. Oheislaitteet voivat myös lähettää ohjaussignaaleja suorittimelle/sen ohjausosalle kertoakseen huomiota vaativasta operaatiosta, esim. käyttäjän tekemästä näppäinpainalluksesta.
Esimerkki. Kuvassa ohjausväylän leveys on 3 bittiä, joten siinä voi olla joko 3 operaatiota tai 2^3 = 8 operaatiota, riippuen siitä miten väylän tulkinta on toteutettu. Perinteisesti voidaan ajatella, että yksi johdin toteuttaa yhden toiminnon, esimerkiksi kuvassa kertoo onko kyseessä muistin luku vai kirjoitusoperaatio.
Muistit¶
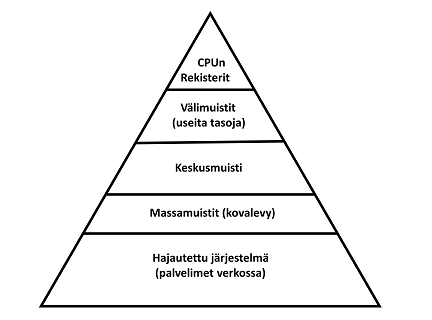
Moderneissa tietokonejärjestelmissä käytetään toiminnan optimoimiseksi useita erityyppisiä muisteja ja lisäksi muistin organisointiin on tarjolla erilaisia ratkaisuja. Tavoitteena on tietysti saada tiedonsiirto muistista suorittimelle ja takaisin mahdollisimman nopeaksi.
Tyypillisesti muistit on organisoitu hierarkiaan, kts kuva alla. Mitä ylempänä hierarkiassa ollaan, sitä kooltaan pienempää, nopeampaa ja kalliimpaa muisti (per bitti) on. Kun muistiin kirjoitetaan / luetaan, tietoalkiot kulkevat hierarkian läpi:
- Ylimmällä tasolla (eli lähinnä CPU:ta) ovat sen omat sisäiset rekisterit
- suorittimen sisällä ja ulkopuolella on useita välimuisteja omassa hierarkiassaan
- keskusmuisti
- massamuisti(t) I/O-väylän takana, kuten kovalevy, tai lopulta palvelimet verkkoyhteyden takana.
Keskusmuisti¶
Keskusmuisti (käyttömuisti, engl. Random access memory, RAM) toimii käskyjen ja prosessoitavan tiedon pääasiallisena säilytyspaikkana ja on kytketty suorittimeen mahdollisimman nopean muistiväylän kautta.
Suorittimen ohjausosa toimii muistin kanssa seuraavasti. Ohjausosa asettaa osoitejohtimille muistipaikan osoitetta vastaavat rinnakkaiset bitit ja kertoo ohjaussignaalilla onko kyseessä luku- vai kirjoitus-operaatio. Lukuoperaatiossa muistin oma ohjausosa hakee tiedon osoitetusta muistipaikasta ja asettaa tietoalkion binäärilukuna dataväylälle, josta suorittimen ohjausosa sen synkronoidusti lukee ja tallentaa suorittimen rekisteriin. Kirjoitusoperaatiossa taas suorittimen ohjausosa asettaa rekisteristä tietoalkion binäärilukuna dataväylälle, josta muistin ohjausosa sen lukee ja vie osoitettuun muistipaikkaan.
Välimuistit¶
Välimuistin idea on säilyttää sellaista tietoa, jota suoritin mahdollisesti seuraavaksi tarvitsisi. Tietysti tällaista tietoa on edullista/nopeaa säilyttää mahdollisimman lähellä suoritinta, josta se olisi nopeasti saatavilla. Suorittimen rekistereitä on yleensä pieni rajallinen määrä, joten välimuisti tuo isomman muistialueen lähelle suoritinta.
Nyt, ohjausosan hakiessa dataa keskusmuistista (kuten yllä on kuvattu), tietoalkio kulkee väylällä välimuistihierarkian läpi ja jää eri välimuisteihin talteen. Itseasiassa, yhdellä muistiosoituksella keskusmuistiin on edullista hakea isompi muistilohko (useita vierekkäisiä muistipaikkoja) eikä yksittäistä tietoalkiota. Tämän operaation voivat muistien ohjausosat neuvotella keskenään. Seurauksena, kun suoritin tarvitsee seuraavan käskyn ja/tai dataa, nämä ovatkin jo välimuistissa odottamassa, eikä hakua tarvitse ulottaa (hitaampaan) keskusmuistiin asti.
Välimuistin optimaalinen hyödyntämisen onkin ihan oma taiteenlajinsa, perustuen ohjausosaan toteutettuihin algoritmeihin, jotka koittavat päätellä mitä tietoa keskusmuistista ohjelma seuraavaksi tarvitsisi. Asiaan palataan kurssin TKJ-osuudessa.
Virtuaalimuisti¶
Nykytyöasemissa ohjelmille tarjotaan niiden oma muistialue, virtuaalimuisti (näennäismuisti, engl. virtual memory), joka koostuu tietokonejärjestelmään liitetyistä erillisistä fyysisistä muisteita, kuten keskusmuistit ja massamuistit. Ohjelmalle tämä erillisistä muisteista koostuva muisti näkyy yhtenäisenä muisrtialueena ohjausosien yhteispelin ansiosta.
Virtuaalimuistin ideana on, että yhtäältä ohjelmille voidaan tarjota keskusmuistia isompia muistialueita ottamalla massamuistia mukaan ja toisaalta keskusmuistia voidaan jakaa samanaikaisesti ajettavien ohjelmien kesken käyttämällä massamuistia (isompana) tietovarastona.
I/O-väylä¶
I/O-väylä (engl. I/O bus) liittää suorittimen toimintaympäristöönsä eli tietokoneen oheislaitteisiin. Tyypillisiä väylään kytkettyjä I/O-laitteita ovat:
- Tiedon säilyttämiseen tarkoitetut laitteet, kuten massamuistit (sisäinen SSD-kovalevy, ulkoiset USB-kovalevyt ja CD/DVD-kirjoittimet).
- Tietokoneen ja ihmisen vuorovaikutuksen mahdollistavat laitteet: näyttö, näppäimistö ja hiiri, jne.
- Liitynnät tietoverkkoihin: lankanetti (Ethernet), langaton Wi-Fi, jne..
Tietokoneen eri väylät kytkeytyvät toisiinsa I/O-siltojen (engl. I/O bridge) kautta. Väylätoteutuksista riippuen väylien leveydet voivat olla erilaisia, niissä eri tiedonsiirtonopeus (esim järjestelmä on hyvinkin nopea vs muut väylät) ja oheislaitteissa eri sanan leveys. Tässä sillat luovat eri tekniikoilla toteutettuen väylien väliin loogiset ja fyysiset yhteydet sovittimien avulla. I/O-silta voi esimerkiksi puskuroida dataa välimuistin tavoin.
Esimerkki. Varsinkin monimutkaisemmissa sulautetuissa järjestelmissä oheiskomponenteilla ja -laitteilla on eri arkkitehtuuri kuin suorittimella. Esimerkiksi suoritin on 32-bittinen, mutta oheislaite 8-bittinen, kuten esimerkiksi lämpötila-anturi.
Kommunikointi I/O-väylän kautta on siis huomattavasti hitaampaa kuin keskusmuistin kanssa. Suoritin jutteleekin I/O-väylän kautta laitteiden kanssa kahdella eri tavalla:
- pollaamalla, eli kysymällä vuoronperään I/O-väylän laitteilta mitä niille kuuluu. Laitteen antama vastaus saattaa vaatia reagointia ohjelmassa, esimerkiksi jos ulkoisesta massamuistista on luettu uutta dataa, niin se kannattaa siirtää keskusmuistiin nopeaan ohjelmien käyttöön.
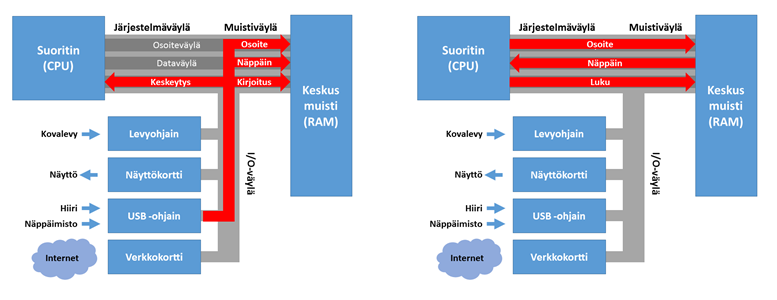
- Oheislaite voi lähettää suorittimelle keskeytyksen eli valitun signaalin ohjausväylässä, joka kertoo että laitteen tilassa on tapahtunut jokin muutos. Suoritin reagoi tähän signaaliin joko firmiksessä (esim. PC:ssä näppäinpainallus) tai ajamassaan ohjelmassa (esim. tulkitsee sulautetun laitteen kosketusnäytön painalluksen).
Jälkimmäinen, keskeytyspohjainen tapa on yleisesti ottaen parempi ohjelman suorituksen kannalta, koska suorittimelle jää aikaa tehdä muutakin kuin vain morjestella hitaita oheislaitteita I/O-väylän kautta ja odotella vastausta. Sulautetuissa järjestelmissä on yleisesti käytössä molempia tapoja, riippuen pitkälti oheislaitteden ja -komponenttien toteutuksesta. Pollaus on usein halvempi tapa toteuttaa sähköisiä komponentteja, kuten erilaisia antureita, koska keskeytyksen lähettämisen ohjauslogiikkaa ei anturissa tarvita.
Esimerkki. Kuvassa alla PC-näppäimistöstä näppäimen painalluksesta lähtenyt keskeytys suoritimmelle, jonka yhteydessä painetun näppäimen koodi tallennetaan näppäimistöajurin muistiin ja eri muistien ohjausosien avulla suoraan sovittuun muistipaikkaan keskusmuistissa. Suoritin sitten reagoi näppäimistöohjaimen lähettämään keskeytyssignaaliin ja lukee painetun näppäimen koodin keskusmuistista. Suoritin ei siis tässä sinällään näe oheislaitteita, vaan operoi suoraan keskusmuistin kanssa.
Lopuksi¶
Tietotekniikan kehitys on viime vuosikymmeninä ollut niin nopeaa, ettei tunnettujen teknologiajohtajien ennustuksetkaan ei aina osu oikeaan..
I think there is a world market for maybe five computers.
- Thomas Watson, chairman of IBM, 1943
- Thomas Watson, chairman of IBM, 1943
There is no reason anyone would want a computer in their home.
- Ken Olsen, chairman of Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC), 1977
- Ken Olsen, chairman of Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC), 1977
Suorittimen ja tietokonejärjestelmän toimintaan palaamme tarkemmin kurssin tietokonetekniikan osuudessa.
Anna palautetta
Kommentteja materiaalista?